A quick summary of Bits and Bites
At the smallest scale in the computer, information is stored as bits and bytes. In this section, we'll look at how that works.
Bit
- a "bit", like an atom, the smallest unit of storage
- A bit stores just a 0 or 1
- "In the computer it's all 0's and 1's" ... bits
- Anything with two separate states can store 1 bit
- -Nick's tennis racket example
- In a chip: electric charge = 0/1
- In a hard drive: spots of North/South magnetism = 0/1
- A bit is too small to be much use
- Group 8 bits together to make 1 byte
Everything in a computer is 0's and 1's ... what does that mean? The bit stores just a 0 or 1 .. it's the smallest building block of storage.
Byte
- One byte = grouping of 8 bits
- e.g. 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0
- One byte can store one character, e.g. 'A' or 'x' or '$'
How Many Patterns With N Bits? (demo)
How many different patterns can be made with 1, 2, or 3 bits?
| Number of bits | Different Patterns |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 1 |
| 2 | 00 01 10 11 |
| 3 | 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 |
- 3 bits vs. 2 bits
- Consider just the leftmost bit
- It can only be 0 or 1
- Leftmost bit is 0, then append 2-bit patterns
- Leftmost bit is 1, then append 2-bit patterns again
- Result ... 3-bits has twice as many patterns as 2-bits
- In general: add 1 bit, double the number of patterns
- 1 bit - 2 patterns
- 2 bits - 4
- 3 bits - 8
- 4 bits - 16
- 5 bits - 32
- 6 bits - 64
- 7 bits - 128
- 8 bits - 256 - one byte
- Mathematically: n bits yields 2n patterns (2 to the nth power)
One Byte - 256 Patterns (demo)
- 1 byte is group of 8 bits
- 8 bits can make 256 different patterns
- How to use the 256 patterns?
- How to store a number in a byte?
- Start with 0, go up, one pattern per number, until run out of patterns
- 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... 254, 255
- One byte can hold a number between 0 and 255
- i.e. with 256 different patterns, we can store a number in the range 0..255
- pixel.setRed(n) takes in a number 0..255. Why?
- The red/green/blue numbers of a pixel are each stored in one byte
Bytes
- "Byte" - unit of information storage
- A document, an image, a movie .. how many bytes?
- 1 byte is enough to hold about 1 typed character, e.g. 'b' or 'X' or '$'
- Later we'll look at storage in: RAM, hard drives, flash drives
- All measured in bytes, despite being very different hardware
- Kilobyte, KB, about 1 thousand bytes
- Megabyte, MB, about 1 million bytes
- Gigabyte, GB, about 1 billion bytes
- Terabyte, TB, about 1 trillion bytes (rare)
The space that data takes up in the computer is measured in by the "byte". One byte is big enough to hold a single typed charater, like 'a'. The capacity of RAM and persistent storage is measured in bytes.
Bytes and Characters - ASCII Code
- ASCII is an encoding representing each typed character by a number
- Each number is stored in one byte (so the number is in 0..255)
- A is 65
- B is 66
- a is 96
- space is 32
- "Unicode" is an encoding for mandarin, greek, arabic, etc. languages, typically 2-bytes per "character"
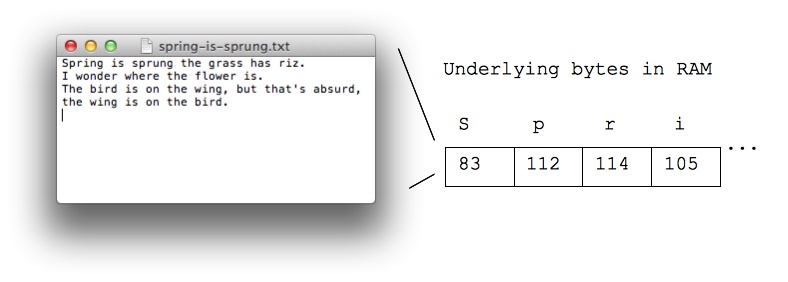
Typing, Bytes, and You
- An example of bytes in your daily life
- When you type letters on your phone or computer
- Each letter is stored in a byte, as below
- 100 typed letters takes up 100 bytes
- When you send, say, a text message, the numbers are sent
- Text is quite compact, using few bytes, compared to images etc.